Servo motor is a motor, which we control by telling it at what angle it should be rotated and servo is trying to maintain that position.
How to work with it
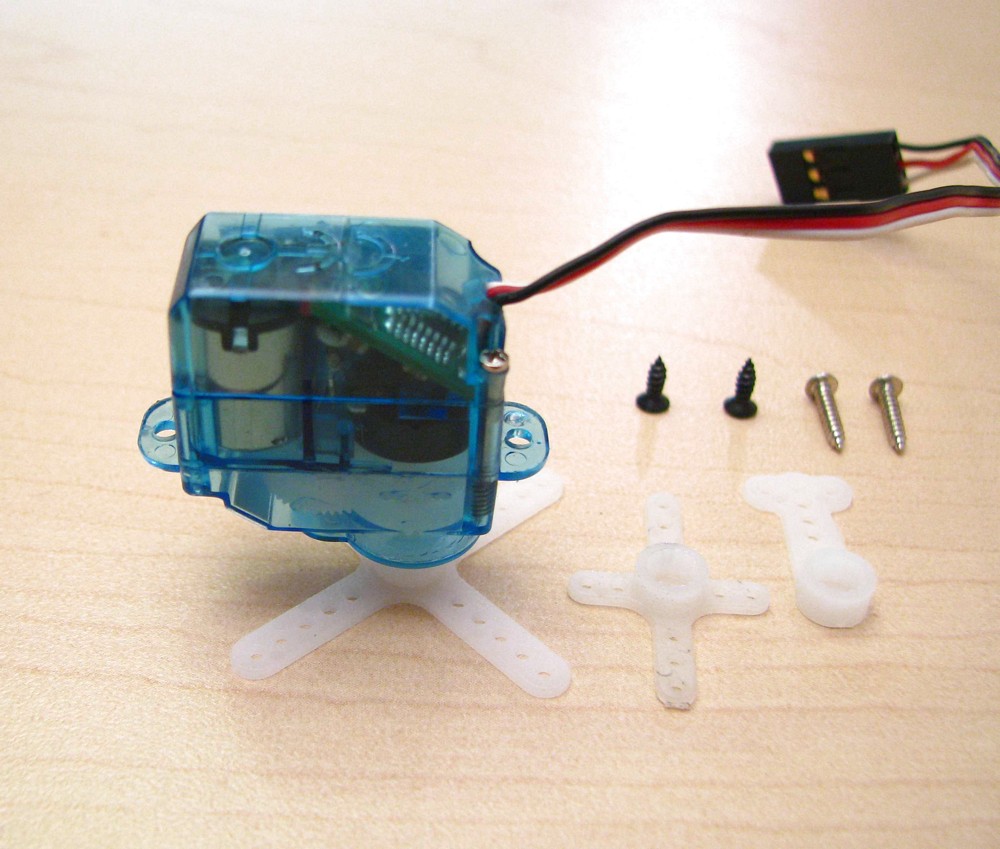
Servo has 3 outputs: Power, Ground and Data.
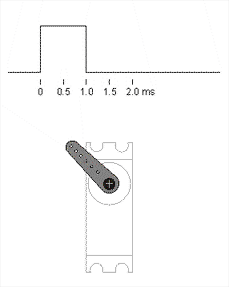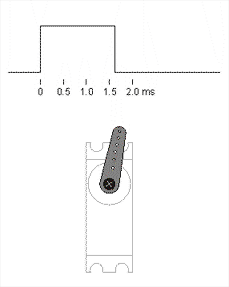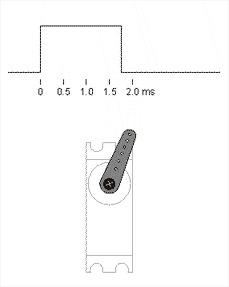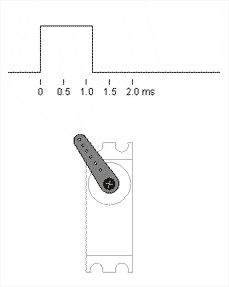
On Data wire we apply PWM signal with different duty cycle, to control our motor.
There are a variety of different servos, so you still need to read datasheet, but this information will help you to start.
Now i will write about their structure, you don't need to know what is inside of them to use them.
Servo motor structure
Output sline and drive gears are conneced with potentiometer, which determines rotation angle. Pot is connected with VCC and GND, middle is connected with control circuit, so we have a voltage divider.
Our PWM signal is telling servo what angle we want by telling what voltage should be on potentiometer middle pin. e.g. we tell servo that we need 5V on ouput, but motor right now is positionned on 0°, so pot output is 0V, electric control circuit in the servo starts to spin motor until pot output is the one we need, in addition it's hard to turn motor from that position, because servo motor control circuit is trying to maintain potentiometer in the same position.
Neutral position is a state when control signal width is equal to a half of the difference between maximum and minimum signal width, in our case it's 1.5 ms == 90°.
Motor usually has high RPM, (rotation speed), but weak torque, so they can't move heavy objects, that's why peoples use transmission, it's a number of gears connected together which decrease output rotating speed, but increase torque. (or vice versa). Actually for controlling servos we don't use PWM, but instead it's more correctly to name that PDM (Pulse Density Modulation).
Characteristics
Torque
In datasheet it's written for 2 voltage values 4.8V and 6V. It tells maximuw weight that servo could hold without rotating. e.g. 15 kg/cm means that servo is able to hold 15 kg on a 1 cm long arm. And it could hold 1 kg on a 15 cm long arm.
Rotation speedServo motors speed is determine by the time it takes motor to rotate from 0° to 60° with 4.6 and 6 V. e.g. 0.06s/60° means that this servo is rotating output spline by 60° in 0.06 s.
Form factor / Size
Servos vary in size. Although there is no official specifications, manufactures stick to several size types:
| Name | Dimensions, mm | Weight, g |
| Micro | 24 x 12 x 24 | 8-10 |
| Mini | 30 x 15 x 35 | 23-25 |
| Normal | 40 x 20 x 37 | 50-80 |
| Giant | 49 x 25 x 40 | 50-90 |
Transmission type / Gears material
plastic, carbon fiber and metal. The differ by weight, durability and price.
Output spline moves with the help of bearings, but they wear out with time.
Motor types
Motor with core average motor with wire winding in the center which rotates, inside there are permanent magnets on the walls, it takes more time for it to change speed moreover it vibrates.
Motor without core permanent magnet inside (not moving), wire winding is around that (rotates), without previous type flaws, but more expensive.
There are also servos with brushless motor, they are the best and the most expensive of all, but not so common.
Analog and digital
Digital servos havemicroprocessor, they are working oh higher frequencies, they have better accuracy, there is no dead zones. But they consume more power and are expensive.
Dead zone is a small zone close to the motor position, it's difficult for a servo to rotate by a small angle, as we remember potentiometer determines at which angle we are right now, when there is small difference in angles, we have small voltage difference between what we need to have on potentiometer and what we actually have, it is not enough to torate the motor.
General info
Motor — a machine that converts electricity into a mechanical motion.
Transmission — gearbox that uses gears and gear trains to provide speed and torque conversions from a rotating power source to another device..
Sources:
Wikipedia
zelectro.com.ua
avmodels.ru
rc-auto.ru
wiki.amperka.ru









No comments :
Post a Comment